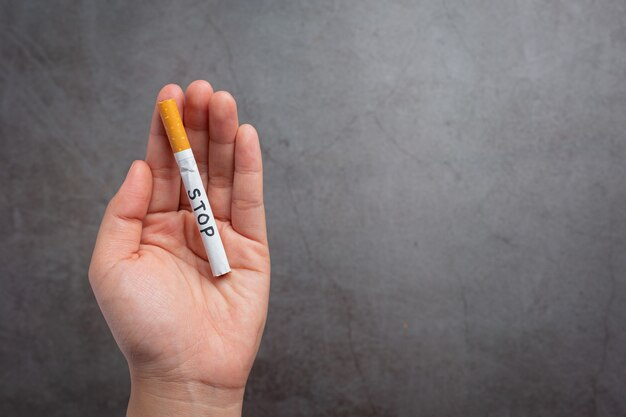
Smoking has long been a habit that people struggle to quit. This article explores the profound impact of smoking on health, delving into the associated risks, and providing valuable insights into quitting smoking strategies. It is a known fact that smoking is injurious to health, but let’s break down the specifics, from the moment you light up that first cigarette to the challenges faced when attempting to quit.
The Start of the Habit: Lighting the First Cigarette
What Happens When You Inhale?
The moment you inhale that first puff, you’re subjecting your body to a host of harmful chemicals, such as tar, nicotine, and carbon monoxide. These chemicals disrupt the normal functioning of your lungs, heart, and brain. Nicotine, in particular, is a highly addictive substance that hooks you into the habit.
From the very first inhalation, you expose your body to a toxic cocktail of chemicals. These compounds are designed to keep you hooked, and their impact on your health is severe. Let’s break down what happens when you take that fateful first puff.
The Dangerous Ingredients
Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, with at least 250 of them recognized as harmful, and more than 50 identified as carcinogens. Some of the most notorious culprits include:
- Nicotine: The highly addictive component that keeps you craving another cigarette.
- Tar: A sticky substance that clings to the lungs, causing respiratory issues.
- Carbon Monoxide: Reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen, putting a strain on the heart and overall health.
The Nicotine Hook
Nicotine is what transforms smoking from an occasional experiment into a full-blown addiction. When inhaled, it travels quickly to the brain, where it stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure. This rush of dopamine creates a sense of euphoria and relaxation, making you crave more. The more you smoke, the more your brain becomes dependent on nicotine to maintain these mood-altering effects.
The Role of Peer Pressure
Why Do People Start Smoking?
Peer pressure is a significant factor that lures individuals into smoking. The need to fit in, look cool, or be part of a social group can lead to that initial puff. Understanding these triggers can be crucial for quitting later on.
Peer pressure is a powerful force, and it often leads people down the path of smoking. The desire to fit in, be part of a group, or just look “cool” can make it hard to resist that first cigarette. It’s essential to understand the underlying factors that push people towards smoking. Let’s explore some of the reasons why individuals start this detrimental habit.
Social Acceptance
In many social circles, smoking is seen as a way to connect with others. Whether it’s a group of friends behind the school bleachers or coworkers during a break, the act of smoking can provide a sense of belonging.
Curiosity
For some, curiosity gets the better of them. They want to see what the fuss is about and end up trying that first cigarette.
Stress and Coping
Stress can be a significant factor, especially among young adults. Smoking is perceived as a way to cope with stress, even though it only provides temporary relief.
Rebellion
Teenagers, in particular, may start smoking as an act of rebellion against authority figures or as a form of self-expression.
Understanding these triggers can be the first step towards quitting. When you recognize why you started smoking, it becomes easier to address those underlying issues during your journey to quit.
Health Risks of Smoking
Lungs in Jeopardy: Respiratory Health
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Long-term smokers often suffer from COPD, a condition characterized by chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The effects on the lungs can be debilitating, making every breath a struggle.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a collective term for a range of lung conditions that cause breathing difficulties. Two of the most common forms are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions result in narrowed airways and damaged lung tissue, making it progressively harder to breathe.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by the inflammation and narrowing of the airways. It leads to a persistent cough, excessive mucus production, and difficulty in breathing. Smokers are at a significantly higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis.
Emphysema
Emphysema occurs when the air sacs in the lungs become damaged and lose their elasticity. This results in a reduction in the surface area available for oxygen exchange, leading to shortness of breath and a feeling of suffocation.
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most lethal consequences of smoking. It accounts for a large percentage of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The carcinogens present in cigarette smoke are a ticking time bomb for lung tissue.
Lung cancer is a devastating diagnosis. It often progresses silently until it reaches an advanced stage, making it challenging to treat. Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, and the risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked and the duration of smoking.
How Smoking Causes Lung Cancer
Cigarette smoke contains a plethora of carcinogens, including tar and various chemicals that can damage the DNA in lung cells. Over time, this damage can accumulate and lead to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells – the hallmark of cancer.
The Cardiovascular Toll
Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Smoking significantly raises the risk of heart disease. It can lead to the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries, reducing blood flow and increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes.
The impact of smoking on cardiovascular health is alarming. It’s a leading cause of preventable heart disease and stroke. The following are the key cardiovascular risks associated with smoking:
Atherosclerosis
Smoking contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Blood Clotting
Smoking increases the likelihood of blood clots forming in the arteries. These clots can block blood flow to the heart or brain, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
High Blood Pressure
Nicotine in cigarettes raises blood pressure, putting additional strain on the heart. Over time, this can lead to hypertension, a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Other Health Complications
The Connection to Diabetes
Research shows a strong link between smoking and diabetes. Smokers are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes due to the adverse effects of smoking on insulin sensitivity.
Smoking and diabetes are a dangerous combination. The toxins in cigarette smoke can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate insulin, a hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar levels. As a result, smokers are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Insulin Resistance
Smoking causes insulin resistance, making it more difficult for cells to respond to insulin’s signals. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels and, over time, can progress to type 2 diabetes.
Reproductive Issues
Smoking can cause infertility in both men and women. Women who smoke during pregnancy are at risk of complications, including premature birth and low birth weight.
Smoking doesn’t just harm the person who smokes; it also affects those around them, particularly during pregnancy. The following reproductive issues are associated with smoking:
Infertility
Both men and women who smoke may experience fertility problems. Smoking can reduce sperm count in men and affect the quality of eggs in women, making it harder to conceive.
Pregnancy Complications
Smoking during pregnancy is linked to a higher risk of complications such as premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. It’s crucial for expectant mothers to quit smoking for the health of both themselves and their babies.
The Psychological Battle
Nicotine Addiction
How Nicotine Alters the Brain
Nicotine triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure. This creates a sense of dependency on smoking to maintain mood and stress levels.
Nicotine is more than just a chemical in cigarettes; it’s a powerful addiction. Understanding how it alters the brain’s chemistry is crucial in appreciating the hold it has on those who smoke.
The Dopamine Rush
When you smoke, nicotine rushes to the brain and stimulates the release of dopamine. This is the pleasure signal – the brain’s way of reinforcing the behavior. Over time, your brain becomes reliant on nicotine to maintain those pleasurable feelings.
Withdrawal Symptoms
When trying to quit, individuals often face withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and strong cravings. These can make quitting seem like an insurmountable challenge.
The idea of quitting smoking can be intimidating, and one of the primary reasons is the fear of withdrawal. The withdrawal symptoms are both physical and psychological and can be highly challenging to overcome. Let’s delve into these symptoms to better understand what you might face on your journey to quitting.
Irritability
Nicotine withdrawal can lead to irritability and mood swings. It’s essential to prepare for these emotional ups and downs during the quitting process.
Anxiety
Many individuals experience heightened anxiety when they attempt to quit smoking. The absence of nicotine can lead to restlessness and nervousness.
Cravings
The cravings for nicotine can be intense, making it difficult to resist the urge to smoke. These cravings are often triggered by certain situations or emotions.
The Role of Habits and Triggers
Identifying Smoking Triggers
Understanding what prompts you to smoke can be the key to quitting. Whether it’s stress, social situations, or simply habit, recognizing these triggers empowers you to break free.
Smoking is not just a physical addiction; it’s also deeply ingrained in your daily habits and routines. Identifying and addressing these triggers is vital in your journey to quit.
Stress and Smoking
For many, stress is a significant trigger for smoking. Recognizing healthier ways to cope with stress is essential when quitting.
Social Situations
Social gatherings, especially those with other smokers, can trigger the desire to smoke. It’s crucial to have a plan for handling these situations without giving in to the temptation.
Habitual Smoking
Smoking can become a habit linked to daily activities, like having a morning coffee or taking a break at work. Identifying these routines can help you break the habit.
Quitting Strategies
Cold Turkey vs. Gradual Reduction
Cold Turkey
Some smokers opt for the abrupt approach, quitting smoking altogether. This method requires strong willpower and determination.
Choosing the right quitting strategy is a personal decision. One of the most debated options is whether to quit cold turkey or gradually reduce your smoking. Let’s examine both approaches and their pros and cons.
Cold Turkey
Quitting cold turkey means giving up smoking entirely and immediately. This approach requires a strong commitment and willpower.
Pros of Cold Turkey
- Quick Results: You experience the health benefits of quitting sooner.
- No Half-Measures: There’s no room for smoking, reducing the risk of relapse.
- Financial Savings: You stop spending money on cigarettes.
Cons of Cold Turkey
- Withdrawal: Withdrawal symptoms can be intense and challenging.
- High Relapse Risk: The abrupt nature can lead to relapses for some individuals.
Gradual Reduction
Gradual reduction involves slowly decreasing the number of cigarettes consumed daily. It can be less challenging for those who find quitting cold turkey too difficult.
Pros of Gradual Reduction
- Less Severe Withdrawal: Smokers may experience milder withdrawal symptoms.
- Psychological Preparation: It provides time to adjust to the idea of quitting.
- Higher Success Rate for Some: Some individuals find it easier to quit this way.
Cons of Gradual Reduction
- Prolonged Exposure: You’re still exposing yourself to the harmful effects of smoking.
- Temptation: It may be harder to resist the temptation to smoke since it’s not an immediate quit.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
Nicotine Gum and Patches
NRT methods like gum and patches help ease the withdrawal symptoms by providing controlled doses of nicotine.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) offers a safer way to get nicotine into your system while you work on quitting. Here are some common NRT methods:
Nicotine Gum
Nicotine gum is chewed to release a controlled dose of nicotine, helping to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Nicotine Patches
Patches are worn on the skin and release a steady amount of nicotine throughout the day. They can be a convenient way to manage cravings.
Pros of NRT
- Controlled Nicotine Intake: NRT products provide a controlled dose of nicotine, reducing the urge to smoke.
- Fewer Withdrawal Symptoms: NRT can ease withdrawal symptoms, making it easier to quit.
- Reduced Risk of Relapse: It increases the chances of successfully quitting.
Cons of NRT
- Cost: NRT products can be expensive, especially if used over an extended period.
- Nicotine Dependency: Some individuals may become dependent on NRT products.
Medications
Prescription Medications
There are prescription medications, like Chantix, that can help reduce the craving for nicotine.
Prescription medications are another option to aid in smoking cessation. Chantix (varenicline) is a medication that can help reduce nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms. It works by affecting the nicotine receptors in the brain, making smoking less satisfying.
Pros of Prescription Medications
- Effective: Medications can significantly reduce the desire to smoke.
- Professional Guidance: They are prescribed by a healthcare provider, who can provide support and monitoring.
Cons of Prescription Medications
- Side Effects: Some medications can have side effects, and not everyone can tolerate them.
- Cost: Medications can be expensive, depending on your healthcare coverage.
Behavioral Support
Counseling and Support Groups
Many individuals find success in quitting by attending counseling sessions or joining support groups. These provide a sense of community and guidance.
Quitting smoking is not just about overcoming a physical addiction; it’s also a psychological and emotional journey. Behavioral support, such as counseling and support groups, can make a significant difference in your ability to quit.
Individual Counseling
Individual counseling provides one-on-one support, allowing you to explore the emotional and psychological aspects of smoking and quitting.
Group Therapy
Support groups offer a sense of community and shared experiences. They can be an excellent source of motivation and encouragement.
Pros of Behavioral Support
- Emotional Assistance: Counseling can help you address the emotional aspects of quitting.
- Accountability: Support groups provide accountability and motivation.
- Sharing Experiences: Interacting with others who are on the same journey can be reassuring.
Cons of Behavioral Support
- Cost and Availability: The accessibility of counseling and support groups may vary depending on your location and healthcare coverage.
Smoking’s impact on health is undeniable, from the first puff to the last. It jeopardizes your respiratory and cardiovascular health, while the psychological battle of nicotine addiction can be excruciating. However, quitting is possible. There are numerous strategies and resources available, making it more attainable than ever. It’s a journey, but one that leads to a healthier, smoke-free life.
Smoking is a dangerous habit that exacts a significant toll on your health. From respiratory issues and heart disease to the psychological clutches of nicotine addiction, the risks are abundant. But the journey towards quitting is a path worth taking. Whether you choose to quit cold turkey, use nicotine replacement therapy, medications, or seek behavioral support, there’s a strategy that can work for you. Remember, quitting is not just about breaking the physical addiction; it’s about reclaiming your health, freedom, and future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best way to quit smoking?
The best way to quit smoking varies from person to person. Some may find success with cold turkey, while others may benefit from nicotine replacement therapy or medication. It’s essential to find a method that suits your individual needs.
How long does it take for the body to recover after quitting smoking?
The body starts to recover almost immediately after quitting. Within days, your sense of taste and smell improve, and over time, lung function can significantly improve. The rate of recovery depends on how long you smoked and your overall health.
Are e-cigarettes a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes?
While e-cigarettes are often marketed as a safer alternative, they are not without risks. The long-term health effects of vaping are still being studied, and they can also be addictive due to nicotine content.
Can secondhand smoke be as harmful as smoking directly?
Yes, exposure to secondhand smoke can be harmful and even deadly. It contains many of the same toxins as direct smoke and can increase the risk of health issues in nonsmokers.
What resources are available for those looking to quit smoking?
There are numerous resources available, including quitlines, online support, apps, and community programs. Many healthcare professionals can provide guidance and support as well. It’s important to seek help when needed, as quitting smoking can be challenging.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional medical advice. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance regarding smoking cessation and its impact on health.

David M is a seasoned author renowned for his expertise in health tips and homemade remedies. With a passion for wellness, he diligently researches and meticulously analyzes a plethora of online resources, ensuring their credibility. David’s dedication shines through as he curates invaluable information, catering to health enthusiasts.